Some borrowers face difficulties understanding the fine line between qualified and nonqualified mortgage requirements. Therefore, brokers are often asked to explain this difference and help their clients choose the most favorable option. So, what fits best: QM vs. Non-QM?
Direct Answer: While Qualified Mortgages (QM) meet strict standards set by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), Non-QM loans do not follow at least one of these requirements and offer more flexible terms. Both loan types ensure that the borrower has the ability to repay the loan – though this ability is defined and documented differently.
QM vs Non-QM in One Table
QM and Non-QM loans vary significantly in terms of underwriting, documentation, DTI requirements, and other features. The following comparison table highlights the key differences clearly:

What Is a Qualified Mortgage (QM)?
Qualified Mortgages (QM) are designed to make the mortgage process clearer and more predictable for all parties. These loans follow CFPB requirements, which provide rules for lenders to help verify that borrowers can repay the loan.
Additionally, the QM framework protects the lender from lawsuits in case a borrower defaults. Most QM loans receive Safe Harbor protection, while more risky mortgages, often with larger loan amounts, have Rebuttable Presumption protection.
To reduce risks for both borrowers and lenders, the CFPB sets QM guardrails. These rules include:
- Points and Fees Cap. A limit on points and fees ensures that the borrower won’t be overcharged and provides transparency in the loan terms.
- No Risky Loan Features. QM loans cannot include negative amortization, balloon payments, or interest-only payments (though limited exceptions apply under certain programs).
- Ability-to-Repay Verification. This core requirement obliges the lender to carefully examine the borrower’s income, assets, and debts to determine whether they can cover mortgage payments.
- Standardized Underwriting. Strict guidelines ensure a predictable workflow in compliance with federal rules.
What is a Non-QM Loan?
Non-QM loans, on the other hand, are mortgages that offer more flexibility for both borrowers and lenders.
With Non-QM loans, borrowers can provide alternative income verification, qualify with higher DTIs or recent minor credit events, and purchase a wider range of properties. Lenders can tailor underwriting guidelines, set their own overlays, and serve borrowers who don’t fit the narrow QM requirements.
The crucial point is that Non-QM loans require thorough ATR verification still, they are not subprime solutions. While underwriting is more flexible, this process remains mandatory and rigorous.
Learn more about Non-QN loan definition.
Why Borrowers “Fail QM” and What Brokers Can Do Next
Many borrowers do not fit strict QM requirements, mostly due to one of the following reasons:
- Non-traditional income patterns, such as unstable income from seasonal or freelance work
- Traditional documentation does not reflect true cash flow. For example, a business owner may have sufficient cash reserves but reinvest profits into the business, keeping personal income low
- Higher DTI due to real-life obligations, like student loans or medical bills, even if cash flow is sufficient to cover mortgage payments
- A recent credit event, such as minor late payments or short-term delinquencies
- A unique property or occupancy scenario, including purchasing non-warrantable condos, mixed-use properties, or second homes with rental income

To check whether the borrower qualifies for a QM loan, brokers should first collect information about the following:
- Income. Traditional documentation, including W-2s, paystubs, and tax returns, is required to verify income and employment.
- Assets. Although QM guidelines do not require reserves, brokers should check whether the borrower has enough savings for a down payment, closing costs, and other expenses.
- Debts. Understanding recurring obligations, such as student loans, credit cards, and medical bills, is crucial for evaluating the debt-to-income (DTI) ratio.
- Credit History. Brokers should review recent credit events and reports to detect late payments, bankruptcies, foreclosures, or other credit issues.
- Property. The purchase agreement and property type must comply with QM and lender guidelines, including meeting habitability standards and passing an appraisal.
When QM is the Better Fit
Generally, QM loans offer the most favorable conditions – lower interest rates, more affordable down payments, faster closing processes, and predictable repayment terms. For that reason, QM loans are often the first option to consider.
So, when are QM loans the best fit?
- The borrower has a consistent employment history and stable W-2 income
- The borrower’s DTI is low and fits QM guidelines
- The documentation is clean and verifies income and assets clearly
- The borrower has a strong credit history, without recent negative events
- The property meets eligibility and occupancy requirements
Broker Best Practice: Pursue a qualified mortgage first when the borrower’s documentation supports it.
When Non-QM Makes Sense
If the borrower is not eligible for a QM loan, review their compliance with Non-QM guidelines. Note that their overall financial profile must be strong, and they must demonstrate the ability to repay the loan.
When should a borrower choose a Non-QM loan?
- The borrower has non-traditional income patterns, such as self-employment or seasonal work
- The borrower’s DTI exceeds QM limits
- The property is not eligible for QM loans, for example, non-warrantable condos or second homes for investment purposes
- The borrower can provide alternative documentation for income verification
- The borrower has recently experienced a minor credit event
Brokers should review the profile as a whole, also considering the compensating factors. Sufficient reserves, a large down payment, stable income, and other factors provide additional proof of the borrower’s financial stability.
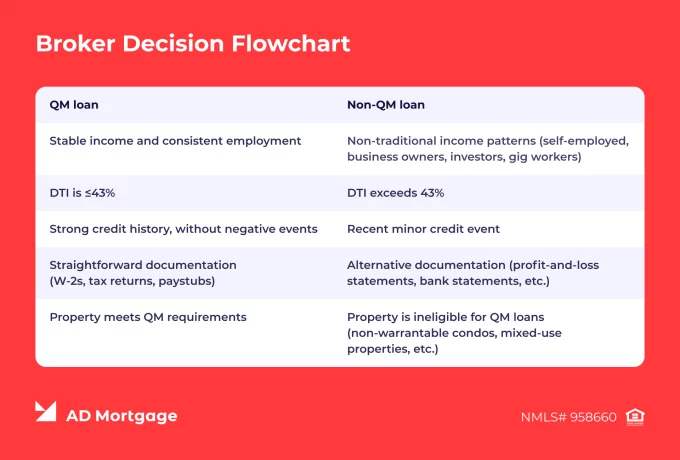
Broker Decision Checklist: Non-QM vs QM Loan
This practical guide helps brokers quickly match a borrower’s situation with the most beneficial loan option:
- Stable income and consistent employment → QM loan
- Non-traditional income patterns (self-employed, business owners, investors, gig workers) → Non-QM loan
- DTI is ≤43% → QM loan
- DTI exceeds 43% → Non-QM loan
- Strong credit history, without negative events → QM loan
- Recent minor credit event → Non-QM loan
- Straightforward documentation (W-2s, tax returns, paystubs) → QM loan
- Alternative documentation (profit-and-loss statements, bank statements, etc.) → Non-QM loan
- Property meets QM requirements → QM loan
- Property is ineligible for QM loans (non-warrantable condos, mixed-use properties, etc.) → Non-QM loan
How AD Mortgage Supports Brokers on Non-QM
AD Mortgage is a Non-QM mortgage lender with over 20 years of experience. Its Non-QM loans offer flexible underwriting, helping our partners serve a wider range of borrowers.
Guidelines vary by program, but credit scores typically start at 620, alternative documentation is accepted, and a minimum level of cash reserves is required.
If your client falls outside of traditional mortgage guidelines, they can still qualify for favorable terms. Submit a loan scenario to receive a solution tailored to your client’s needs.
FAQ: Qualified Mortgage vs Non-Qualified Mortgage
What Does QM Mean in Mortgages?
QM stands for Qualified Mortgage, a type of traditional mortgage that complies with strict standards set by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB). Because of these guidelines, QM loans are generally considered less risky for both borrowers and lenders.
What Does Non-QM Mean?
Non-QM loans do not meet at least one of the CFPB’s QM standards. They typically offer greater underwriting flexibility, helping borrowers achieve homeownership when they can afford it.
Is Non-QM the Same as Subprime?
No. Despite their flexibility, Non-QM loans still require a strong overall financial profile and documented ability to repay the loan.
Do Non-QM Loans Verify Income?
Yes. Non-QM loans do verify income, but they allow alternative documentation to meet this requirement. This approach helps borrowers with non-traditional income patterns, such as self-employed individuals or business owners, qualify for a loan when they don’t fit strict QM documentation standards.
Are Non-QM Loans Legal in the U.S.?
Yes. Non-QM loans are completely legal in the U.S.
Why Do Non-QM Loans Often Cost More?
Compared to traditional loans, Non-QM solutions typically come with higher interest rates, larger down payments, and additional costs. This happens because of more complex underwriting, higher perceived risk for lenders, and increased operational expenses.
Can Borrowers Refinance from Non-QM to QM Later?
Yes. If the borrower meets QM guidelines, they can refinance the loan. This helps them secure lower interest rates, stronger consumer protections, and more predictable terms.
What Should Brokers Collect First to Pre-Qual a Non-QM Scenario?
Brokers should collect information about income, debts, assets, credit history, property, and compensating factors. Then, submit a scenario request to match the client with the right loan program.
Fill out the short form and get a call from our AE
Struggling with a loan scenario?
Get a solution in 30 minutes!