
In 2024, nearly 1 in 5 homebuyers chose an FHA loan to finance their purchase, making it one of the most popular paths to homeownership in the United States. This is especially true for U.S. buyers with low credit scores or limited savings for a down payment.
What does that mean for you in 2025?
Whether you’re a first-time homebuyer, recovering from financial setbacks, or looking for a lower-cost entry into the housing market, FHA loans remain a flexible option. The Federal Housing Administration, under the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), insures these loans, which aren’t to be confused with lending money themselves.
Let’s break down the updated FHA loan requirements, loan limits, and how mortgage insurance premiums work in 2025. AD Mortgage explains who qualifies, program goals, and how FHA loans compare to conventional mortgages. Whether exploring financing options or assisting clients to navigate the housing market, this guide clarifies everything you need to know about FHA financing.
What is an FHA Loan and How Does It Work in 2025?
An FHA loan is a government-backed home loan that allows qualified borrowers to buy or refinance a principal residence with more lenient credit and income criteria than a conventional mortgage. It is unique because the Federal Housing Administration doesn’t issue loans; it insures them. That insurance reduces risk for FHA-approved lenders, encouraging them to work with borrowers who may otherwise struggle to qualify or come up with a down payment.
In 2025, FHA loans continue to be popular due to their smaller down payment requirement, which is 3.5% for borrowers with a credit score of 580 or higher. Those with scores as low as 500 may qualify by making a 10% down payment. These flexible terms open doors for moderate-income families and buyers with low credit scores to access a home loan.
Borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums, upfront and annually. A mortgage insured loan protects the mortgage lender if a borrower defaults. These premiums, combined with affordable terms and predictable monthly payments, make FHA loans attractive despite their added expenses over time.
Federal Housing Administration (FHA): Role, Mission, and Oversight
The Federal Housing Administration was founded in 1934 during the Great Depression to stimulate the housing market. Today, its primary mission remains to promote homeownership for Americans by insuring mortgages issued by FHA loan lenders. In doing so, the FHA reduces individual lenders’ financial risk, especially when working with borrowers who don’t meet traditional conventional loan requirements.

As a division of the United States Department of Housing and Urban Development, the FHA is regulated at the federal government level and follows strict oversight procedures to ensure the long-term sustainability of its loan programs. In 2023, the FHA insured over 1.3 million mortgages, providing over $348 billion in FHA loan volume.
The Federal Housing Administration offers various loan types, including standard home loans, the FHA energy-efficient mortgage, and the home equity conversion mortgage (HECM). FHA has supported first-time homebuyers, veterans, older people, and families with limited income, while maintaining fiscal responsibility through self-funded mortgage insurance structures.
FHA Loan Requirements for 2025: What FHA Loans Require from Borrowers
To be eligible for an FHA loan, borrowers must meet various financial and legal standards demonstrating creditworthiness, income stability, and intent to occupy the property as a principal residence. The Federal Housing Administration doesn’t underwrite these loans directly, but it sets the baseline credit conditions for all FHA-approved lenders to follow. Understanding these FHA loan requirements is essential for a successful application.
In 2025, borrowers must provide verifiable income through pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements, and show a debt-to-income (DTI) ratio below 43%. Proof of U.S. residency and a valid Social Security number are required. The property must meet FHA loan guidelines for safety and livability and be used as the borrower’s (primary) principal residence.
In default cases, all borrowers must pay mortgage insurance premiums to protect the lender. These insurance costs, closing costs, property taxes, and a down payment should be considered when calculating affordability.
Minimum Credit Score and Other FHA Guidelines You Need to Know
- A credit score of 580+ qualifies you for the minimum 3.5% down payment.
- Scores between 500–579 require at least 10% down.
- Scores below 500 generally don’t meet the requirements.
- Lenders check credit reports from all three agencies during evaluation.
- Following bankruptcy, borrowers must wait 2 years. After foreclosure, 3.
- Proven good credit demonstrated by rent or utility bills can help borderline applicants.
How Much Down Payment Do You Need for an FHA Home Loan?
- FHA loans require only a 3.5% down payment with a credit score of 580 or higher.
- A 10% down payment is needed for borrowers with a credit score between 500-579.
- Your down payment can come from a financial gift or payment assistance programs.
- The required down payment percentage is based on the purchase price.
- All funds must be adequately documented to meet the guidelines.
FHA Loan Limits by County: 2025 Updates and Maximum Loan Amounts
- FHA loan limits vary by county and property size.
- The 2025 base loan amount for a single-family home is $524,225.
- In high-cost areas, limits go up to $1,149,825.
- Larger properties (2–4 units) have higher limits.
- Check your local limits using HUD’s online tool.
- Staying within these limits make certain your mortgage stays FHA-insured.
First-Time Homebuyers and Moderate-Income Families: Why FHA Financing Works
Did you know 82% of all FHA purchase loans in 2023 were first-time buyers?
Buying your first home can feel like a financial mountain climb, but the FHA loan program gives first-time homebuyers and moderate-income families the ability to reach the summit. The Federal Housing Administration makes homeownership more than a dream with flexible credit requirements and small down payment options.
Unlike conventional loans that expect spotless credit and an abundant bank account, FHA loans welcome buyers with low credit scores and limited savings. The down payment can also be covered by a financial gift or local payment assistance program, meaning more buyers can become homeowners without emptying their pockets.
The result is a more affordable path to owning a principal residence, especially in a market where home prices continue to rise.
Using FHA Loans for Single-Family Homes, Repairs, and Energy-Efficient Home Improvements
An FHA loan does more than get you in the front door. It also helps you fix the roof, update the kitchen, and reduce energy expenses. While most people consider those for buying a single-family home, the Federal Housing Administration offers options for repairs and energy-efficient home improvements.
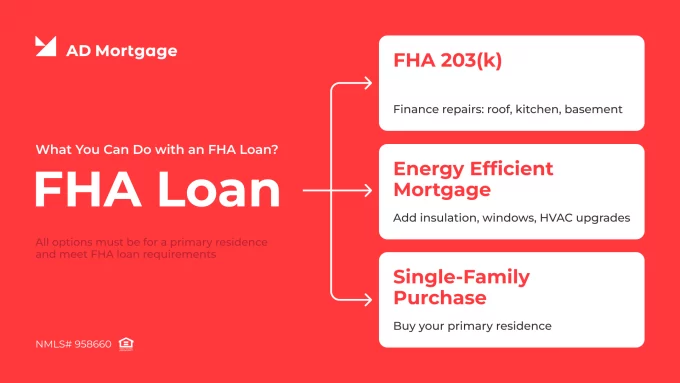
The FHA loan 203(k) program is a homebuyer’s solution if the home of your dreams has a leaky basement or old, musty carpet that needs to go. The program allows you to finance home repairs into the mortgage; with no need to max out your credit cards or take a second loan. Perhaps you want to make your home greener. On the flip side, do you want to make your home greener? The FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage lets you roll the cost of upgrades (windows, insulation, HVAC, etc.) into your loan without increasing your down payment.
All of these options must be used on a principal residence, and the home needs to meet basic requirements. These are excellent solutions for low-to-moderate income families who want to buy confidently and live smarter.
FHA Offers for 2025: Reverse Mortgage, Home Equity Conversion, and Payment Assistance Programs
Beyond helping buyers get into their first homes, the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) supports homeowners across various life stages, whether aging in place or struggling with upfront expenses. In 2025, the FHA loan program includes several underused but powerful options designed to expand flexibility and access.
For example:
- The reverse mortgage, officially called a home equity conversion mortgage (HECM), is available to homeowners aged 62 and older.
Instead of making monthly payments, eligible borrowers can access their home equity through a lump sum, monthly disbursements, or a credit line. The loan is only repaid when the homeowner sells the home, moves out, or passes away.
This program is ideal for retirees who want to age in place while supplementing their income. Unlike a conventional loan, there’s no income requirement, making it more accessible to older people with limited cash flow. As of 2024, more than 500,000 households have used the FHA’s HECM program to remain financially stable in retirement. - For new buyers, there are payment assistance programs to help with upfront costs and down payments. These local and state-backed resources often cover part or all of the down payment and closing costs, making an FHA loan more affordable.
Most programs target moderate-income families and first-time homebuyers, and eligibility typically depends on income and credit score. However, when combined with FHA’s flexible terms, these programs can significantly reduce out-of-pocket expenses, sometimes by thousands of dollars.
FHA Loans Provided by AD Mortgage
- FHA Standard. This program helps you qualify homebuyers with limited down payment capabilities.
- FHA High Balance. A mortgage option that allows for larger loan amounts in high-cost areas.
- FHA Streamline Refinance. Current refinance solution with minimal paperwork, which makes the process faster and easier.
Conclusion
Enhanced Broker Portal
that makes your job easier
- All operations at your fingertips
- Easy-to-use intuitive interface
- Integrated AI technology
In 2025, the FHA loan offers flexible down payment options, lower credit score requirements, and access to programs like the FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage and home equity conversion mortgage. Backed by the Federal Housing Administration, it remains a wise choice for first-time homebuyers, low-to-moderate-income families, and those seeking an easier, more affordable path to owning a home.
Start your journey with AD Mortgage now!
FAQ
What is the downside of an FHA loan?
The main downside of an FHA loan is the added cost of mortgage insurance premiums, which apply for the life of the loan. Even with a smaller down payment, that extra expense can outweigh the benefits.
How do you qualify for an FHA loan in different states?
While the Federal Housing Administration sets FHA loan requirements, individual lenders and state-level housing and urban development programs may have additional guidelines. Always check with FHA-approved lenders in your area.
What would the minimum down payment be for an FHA loan of $250,000?
With a credit score of 580 or higher, your down payment on a $250,000 FHA loan would be $8,750 (3.5%). Lower credit scores require a 10% down payment, or $25,000.
How much should I earn to buy a $300,000 house with an FHA loan?
To afford a $300,000 FHA home loan, aim for a household income of around $70,000–$80,000. This depends on your debts, monthly payments, mortgage insurance, and loan term.
Does the Federal Housing Administration make loans directly?
No, the Federal Housing Administration does not issue loans. Instead, it insures them through the FHA loan program, encouraging private lenders to work with borrowers who might not qualify otherwise.
What is the difference between HUD and FHA loans?
HUD oversees the Federal Housing Administration, but they’re not interchangeable. The FHA loan program is one of HUD’s initiatives. Therefore, while all FHA loans fall under HUD, not all HUD housing programs are loans.
What is the FHA 12-month rule?
The FHA 12-month rule requires borrowers to have made on-time housing payments for the past year. During that time, missed rent or mortgage payments can disqualify you from an FHA loan approval.


